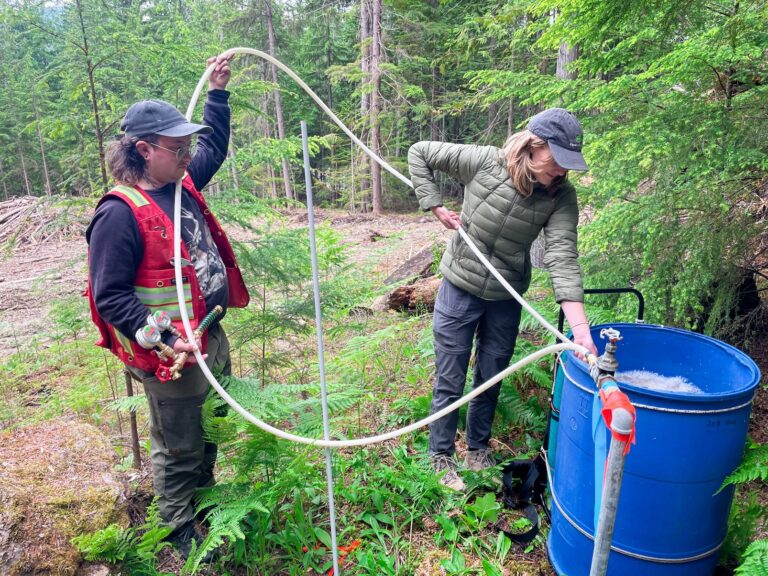
Carleton University is taking extra measures to ensure the safety of staff and students. Since September 2020, Banu Örmeci has added to these efforts by testing the campus’ wastewater for genetic traces of COVID-19.
“We have the technology to identify and warn people who were in contact with a positive case,” said Örmeci, professor in Carleton’s Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering. “But to actually find and connect with them, and to do so quickly, does take a lot of effort.”
Örmeci, the Jarislowsky Chair in Water and Global Health and director of the university’s Global Water Institute, has kept a close eye on campus. Despite the massive move to online learning and teaching, Carleton still hosts several hundred students and essential staff every day.
In four weeks of testing, Örmeci hasn’t detected any spikes in COVID-19 viral RNA in the campus’ wastewater. The wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) testing is conducted weekly, with plans to increase sampling to every few days.
WBE testing can be a discreet, precautionary alert system. Sampling the wastewater leaving campus tests the entire campus population for traces of the coronavirus, and it can be detected earlier than nasal diagnostic tests do.
The WBE method has already helped other universities prevent outbreaks on their campuses. In the first weeks of the fall term, the University of Arizona in Tucson detected levels of COVID-19 in wastewater leaving its residences. It narrowed it down to the building and conducted rapid diagnostic testing on all the students. Two positive cases were identified and an outbreak was avoided.
“It’s a priority of the university to ensure the safety of the Carleton community,” said Örmeci. “We have adopted a tiered approach to test wastewater collected from the whole campus and narrow down our tests if we see an increase.”
Örmeci’s research group measures the quantity of COVID-19’s genetic material in the campus wastewater. If the monitoring indicates an increase, Örmeci and her team would immediately inform campus administrators and public health officials. They would then take samples from specific buildings of importance, such as the residences, the research buildings, and the athletics facilities.
This effort focuses solely on Carleton campus but Örmeci has also been involved in the testing efforts through the City of Ottawa’s sewer system in collaboration with Ottawa Public Health.
Additionally, she is a member of the Canadian Water Network COVID-19 Wastewater Coalition, a coordinated response to the pandemic from wastewater researchers, laboratories, utilities, and public health authorities. The coalition shares knowledge among its members to ensure that WBE results are scientifically-rigorous and useful to public health authorities.
Örmeci is also involved with the International Water Association COVID-19 Taskforce, which shares new studies and applied research methods for the entire water sector, from safe drinking supply to water reuse.
Header Image Credit: CDC.